What is eczema?
Eczema is another term for a skin rash or dermatitis. Many cases start out very itchy with a weeping rash or even blisters, which most likely led to the name eczema. The word eczema comes from the Greek word ekzein, meaning ‘to boil out.’ Eczema may begin in infancy or the first rash may not appear until you are an adult. While many people use the term eczema to describe any skin rash, some use the term to specifically describe atopic dermatitis. We will list many types of dermatitis below.
Is eczema contagious?
Eczema is not contagious and cannot be spread to another person.
Does eczema last forever?
It depends on the type of eczema. Some people have flares that come and go while others may have only ever had one isolated incident. The long lasting, or chronic forms of eczema, can last a long time. Chronic eczema may be less itchy, more irritating and even painful as the skin becomes thick or cracked.
What causes eczema?
The specific cause is unknown but the condition likely develops due to a combination of hereditary and environmental factors. For one type of eczema, atopic dermatitis, It is known that if a parent has this form of eczema then their child has an increased chance of developing atopic dermatitis as well. The odds are even higher if both parents have atopic dermatitis so a genetic component exists. Environmental factors include known irritants, allergens, microbes, very hot or very cold temperatures, foods, stress and hormones.
What is atopic dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is one of the most common and severe form of eczema affecting over 17 million Americans. Atopic dermatitis often affects the cheeks and parts of the arms or legs but can be widespread. Many patients have other problems such as asthma and hay fever (allergic rhinitis) which can be hereditary and run in families. Most affected people develop this process as a child but adults can develop this as well. Many healthcare professionals call atopic dermatitis, “the itch that rashes” because you may start off with just the sensation to itch without a rash. However, once you scratch or rub the rash will then erupt. People with atopic dermatitis typically have sensitive skin that is easily irritated and at a higher risk to become infected. Some patients have this process come and go into adulthood but many children outgrow their eczema as they become adults.
What is contact dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is another common form of eczema that occurs when the affected skin comes into contact with another object or chemical. This may result in an allergic reaction or an irritant type reaction. The classic allergic contact dermatitis is extremely itchy, such as poison ivy, and involves your immune system response. Other types of allergic contact dermatitis can be from metal in your clothing or jewelry, fragrances, soaps, and cosmetics. In contrast, irritant contact dermatitis may burn or itch and does not need to activate the immune system or memory cells. Irritant contact dermatitis could be a rash from an acid that comes into contact with your skin. This may hurt, burn, or itch and is a direct result of the acid in this case. In some cases, patch testing is recommended to isolate the problem. Patch testing is a process to test your skin for common allergens.
What is hand eczema?
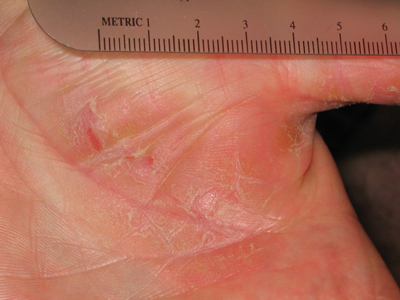 Hand dermatitis is a rash on the hands or fingers that is a common problem affecting up to 10% of Americans. It can be mild or severe, itchy or even painful. People that work in catering, cleaning, hairdressing, healthcare, and mechanical jobs are more commonly affected because they come into contact with more chemicals and irritants. Eczema is not contagious and you can’t catch it from someone else. It can be an allergic reaction or an irritant reaction (see contact dermatitis above). Gentle skin care is recommended with a safe gentle soap, warm water (not hot), followed by a safe moisturizer.
Hand dermatitis is a rash on the hands or fingers that is a common problem affecting up to 10% of Americans. It can be mild or severe, itchy or even painful. People that work in catering, cleaning, hairdressing, healthcare, and mechanical jobs are more commonly affected because they come into contact with more chemicals and irritants. Eczema is not contagious and you can’t catch it from someone else. It can be an allergic reaction or an irritant reaction (see contact dermatitis above). Gentle skin care is recommended with a safe gentle soap, warm water (not hot), followed by a safe moisturizer.
Improving your skin hydration with emollients throughout the day is important to reduce symptoms and reduce recurrences.
What other types of eczema are there?
There are many special types of eczema, and they can include asteatotic eczema , dyshidrotic eczema, neurodermatitis, nummular dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and stasis dermatitis among others. While many of these entities overlap there are absolute distinct clinical and historical characteristics along with treatment approaches to each diagnosis. DSI recommends a consultation to review your specific medical history and physical exam to ensure the correct diagnosis and management.
What is the treatment for eczema?
Eczema can be frustrating and uncomfortable leading to loss of sleep, infection, and scarring. We cannot overemphasize the need to avoid scratching, which worsens the condition. Scratching leads to increased inflammation, weeping of fluid, swelling, cracking, crusting, scarring and perpetuates the itch-scratch cycle.
Other aspects of therapy should include emollients, minimizing environment factors, and education of the disease process. At DSI, we not only treat these aggravating symptoms to alleviate your immediate discomfort but we also provide counselling to the exact process that is causing your rash as well as optimizing your routine skin care to minimize your risk of future reccurrences.
More reading on Eczema
For more information on eczema, please visit:
